Introduction
Interleukin-6 (IL-6) is a cytokine, a signaling molecule involved in the immune system's response and inflammatory processes. Chronically elevated IL-6 levels are linked to the development of various inflammatory diseases. This review examines the rationale for targeting IL-6 for therapeutic intervention and discusses the development of novel therapeutic strategies, including monoclonal antibodies and JAK inhibitors. Additionally, the potential benefits and future directions of IL-6-targeted therapies are addressed.
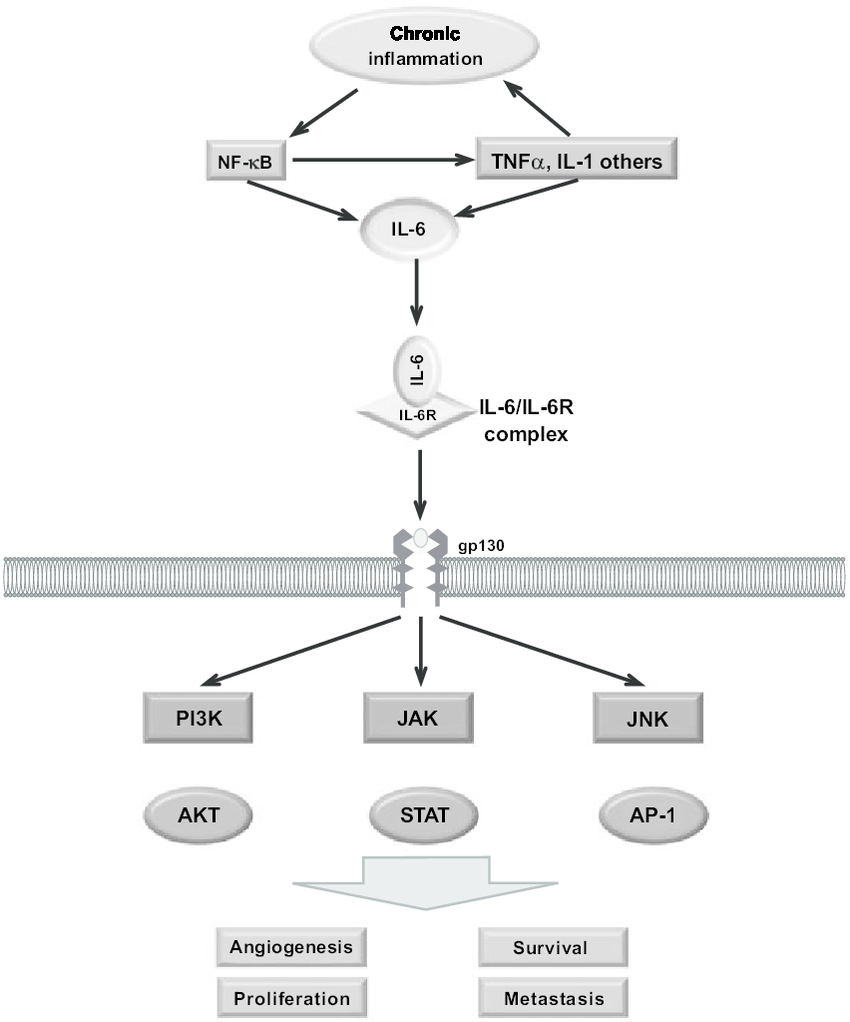
IL-6 and Chronic Inflammation
IL-6 functions as a pro-inflammatory cytokine, promoting the activation and differentiation of immune cells and the production of other inflammatory molecules. While its role in initiating a healthy acute inflammatory response is critical, uncontrolled IL-6 signaling contributes to chronic inflammatory states observed in several diseases.
Diseases Associated with Elevated IL-6
Increased IL-6 levels have been associated with the development and progression of various inflammatory disorders, such as:
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)
- Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD)
- Atherosclerosis
- Neurodegenerative diseases (Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease)
- Certain cancers (colorectal cancer, prostate cancer)
Therapeutic Strategies Targeting IL-6
Two main approaches have emerged for targeting IL-6 in therapeutic interventions:
- Monoclonal Antibodies: These engineered proteins bind specifically to IL-6, preventing its interaction with the IL-6 receptor and subsequent activation of intracellular signaling pathways. Examples include tocilizumab, sarilumab, and claudinsulin.
- JAK Inhibitors: Janus kinases (JAKs) are enzymes involved in IL-6 signaling. JAK inhibitors block the phosphorylation of downstream signaling molecules, thereby suppressing the inflammatory response triggered by IL-6. Examples include baricitinib, tofacitinib, and ruxolitinib.
However, for research purposes, accurately measuring IL-6 levels is crucial. Suppliers like Gentaur offer a reliable and quantitative tools like Human IL-6 ELISA Kit to detect IL-6 in biological samples. This allows researchers to investigate the role of IL-6 in various diseases, assess the efficacy of therapeutic interventions targeting IL-6, and develop new diagnostic approaches.
Advantages of IL-6 Targeting Therapies
Compared to traditional anti-inflammatory drugs, IL-6-targeted therapies offer potential advantages:
- Specificity: By targeting a specific cytokine, these drugs minimize side effects associated with broad-spectrum immunosuppression.
- Improved Disease Management: Clinical trials have shown promising results in reducing disease activity, improving clinical outcomes, and enhancing patient quality of life in various inflammatory conditions.
- Potential for Personalized Medicine: Identifying patients with specific IL-6 profiles might allow for personalized treatment approaches, tailoring therapy based on individual needs.
Future Directions of IL-6 Targeting Therapies
Research continues to explore the therapeutic potential of targeting IL-6, including:
- Combination Therapy: Combining IL-6-targeted drugs with existing medications could potentially lead to combined effects and improved therapeutic efficacy.
- Identifying New Targets: Investigating molecules further downstream in the IL-6 signaling pathway could lead to the development of even more specific therapeutic interventions.
- Targeting IL-6 in Psychiatric Disorders: Emerging evidence suggests a link between IL-6 and depression; exploring the potential of IL-6 targeting therapies in this area warrants further investigation.
Conclusion
Targeting IL-6 represents a promising and rapidly evolving therapeutic approach for managing chronic inflammatory diseases. The development of monoclonal antibodies and JAK inhibitors offers new avenues for treatment with improved efficacy and potentially reduced side effects. Continued research into combination therapies, novel targets within the IL-6 signaling pathway, and exploration of IL-6's role in psychiatric disorders hold the promise for even more effective therapeutic strategies in the future.
To learn more about the role of IL-6 in the immune system and its potential as a therapeutic target, watch this video: