Introduction
L'analyse des acides organiques urinaires (AOu) est essentielle pour le diagnostic et le suivi de diverses maladies, notamment les troubles métaboliques héréditaires, les intoxications et d'autres conditions pathologiques. L'arrivée de la chromatographie liquide couplée à la spectrométrie de masse en tandem (LC-MS/MS) a révolutionné l'analyse des AOu, offrant une précision, une sensibilité et une spécificité inégalées. Les kits d'analyse LC-MS/MS d'acides organiques urinaires ont fourni une solution standardisée et pratique pour les laboratoires cliniques et de recherche, facilitant l'identification et la quantification d'un large éventail de métabolites.
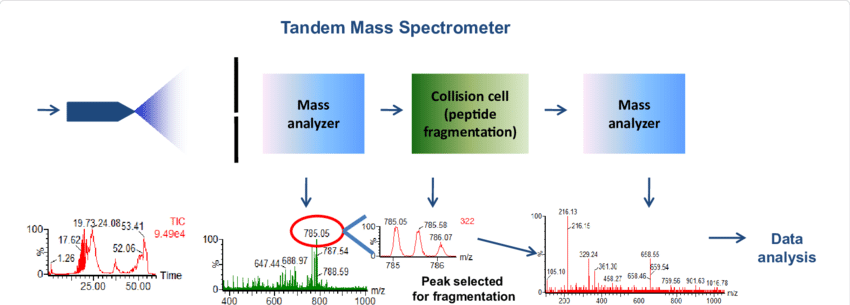
Fonctionnement de l'analyse LC-MS/MS
L'analyse LC-MS/MS des AOu repose sur deux étapes :
- Séparation des composés : La chromatographie liquide (LC) sépare les AOu en fonction de leurs propriétés physico-chimiques.
- Identification et quantification : La spectrométrie de masse en tandem (MS/MS) fragmente ensuite les molécules individuelles en ions caractéristiques, permettant une identification précise et une quantification de chaque métabolite.
Avantages de l'analyse LC-MS/MS
L'analyse LC-MS/MS d'acides organiques urinaires présente de nombreux avantages par rapport aux méthodes traditionnelles :
- Haute sensibilité : Détection d'infimes concentrations d'AOu, même en présence d'interférences.
- Haute spécificité : Identification précise des AOu grâce à la fragmentation MS/MS, minimisant les faux positifs.
- Large plage dynamique : Quantification d'un large éventail de concentrations d'AOu, des valeurs physiologiques aux niveaux toxiques.
- Analyse simultanée de multiples AOu : Identification et quantification de dizaines d'AOu simultanément dans un seul run LC-MS/MS.
Applications de l'analyse LC-MS/MS
L'analyse LC-MS/MS d'acides organiques urinaires trouve son application dans divers domaines :
- Diagnostic des troubles métaboliques héréditaires : Outil essentiel pour le diagnostic et le suivi de nombreuses maladies métaboliques héréditaires, telles que la phénylcétonurie, la maladie urinaire sucrée et l'homocystinurie.
- Surveillance des intoxications : Permet d'identifier et de quantifier les substances toxiques ingérées, favorisant une prise en charge médicale rapide et appropriée.
- Recherche métabolique : Fournit des informations précieuses sur les processus métaboliques dans divers états physiologiques et pathologiques.
Conclusion
L'analyse LC-MS/MS d'acides organiques urinaires est devenue un outil indispensable pour la recherche métabolique, offrant une sensibilité, une spécificité et une précision inégalées. Les kits d'analyse LC-MS/MS d'acides organiques urinaires ont standardisé et facilité cette analyse, la rendant accessible à un large éventail de laboratoires cliniques et de recherche.